Introduction
In the financial year 2023-24, India exported goods and services worth over $770 billion (₹64 lakh crore). This impressive figure not only highlights the country’s strong trade strength but also underscores the critical role of compliance and documentation in ensuring that each export is accounted for.
And one such compliance measure is the issuance of a BRC or Bank Realisation Certificate, a document that officiates your export deal. But what is BRC certification, and why is it important?
Let’s understand what is the meaning of BRC and how it is crucial in any export deal.
What is a Bank Realisation Certificate (BRC)?
A Bank Realisation Certificate (BRC) is a crucial document that acts as a proof of the receipt of payment for your exports. A BRC is issued by an authorised bank, confirming that the payment for the export has been received in India.
Simply speaking, it’s an official proof stating that you have been paid for your exports. Once the money is credited to the exporter’s account, the bank generates this BRC.
Why is a Bank Realisation Certificate (BRC) necessary?
A BRC or Bank Realisation Certificate is a document confirming that the export deal is complete and compliant with Reserve Bank of India (RBI) norms. Here is why BRC is important:
1. Mandatory for export incentives: The BRC is essential to claim benefits under various government schemes, including Duty Drawback, the Service Export from India Scheme (SEIS), and the Merchandise Exports from India Scheme (MEIS).
2. Proof of export payment: The document confirms that you have received payment in foreign currency for goods and services exported. Without a BRC, the transaction is not considered settled by the banks or RBI.
3. Compliance with RBI and DGFT: According to the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) and Reserve Bank of India (RBI) norms, all export earnings must be repatriated and realised within a specific period. Your BRC ensures this compliance.
4. Essential for audits: The BRC serves as a verifiable financial record of foreign income for government audits, income tax filings, or internal company audits.
Why is BRC a significant document for exporters?
BRC helps exporters claim incentives while ensuring compliance and audit readiness. Here is why bank realisation certificate or BRC is needed by exporters:
1. Improves transparency: BRC provides a clear statement of the global transactions, enhancing trust and accountability in international trade. It provides regulators, banks, and other stakeholders with a clear, verifiable view of foreign exchange inflows.
2. Facilitates exchange management: Accurate documentation of export earnings is essential for effective foreign exchange management. BRC simplifies this by providing a reliable record of foreign currency inflows, enabling better tracking, reporting, and control over your export transactions.
3. Makes exporters compliance ready: To be legally compliant, exporters have to show BRC as a proof of payment. This guarantees that there is no risk of non-compliance for exporters that may lead to any penalties.
Why does RBI need BRC?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) relies on BRC to ensure that the payments for the exported goods and services are received in the country. Here is why RBI needs a bank realisation certificate:
1. Export data verification: The BRC or Bank Realisation Certificate helps the RBI and DGFT verify if export transactions have been paid for. This supports accuracy in India’s export and import statistics.
2. Foreign exchange monitoring: BRC acts as a confirmation of proceeds received by the exporter. This enables the RBI to maintain accurate and up-to-date foreign exchange data and manage the balance of payments.
3. Policy formulation: Verified and valid export earnings, as evidenced by a bank realisation certificate (BRC), enable the RBI to design monetary policies, manage currency stability, and make informed decisions related to economic planning.
4. Prevention of export fraud: The BRC also prevents exporters from making false claims against shipments or illegally participating in export incentive schemes. This further helps in tracking illegal activities, such as money laundering and smuggling.
What is e-BRC?
An e-BRC is a digital version of a Bank Realisation Certificate. Earlier, exporters had to visit their banks and apply for a BRC, which was a tedious process. However, in 2012, the DGFT introduced the concept of e-BRC. This moved the entire BRC issuance process online, making it faster, easier, and more efficient.
This allows exporters to access BRC easily without the hassle of waiting for banks to issue it. It has completely streamlined the export process, ensuring transparency, accuracy, and easier compliance with regulations.
How does e-BRC work?
The e-BRC has modified the earlier manual system of how BRC used to work. Here is a step-by-step breakdown to help you understand the workings of e-BRC:
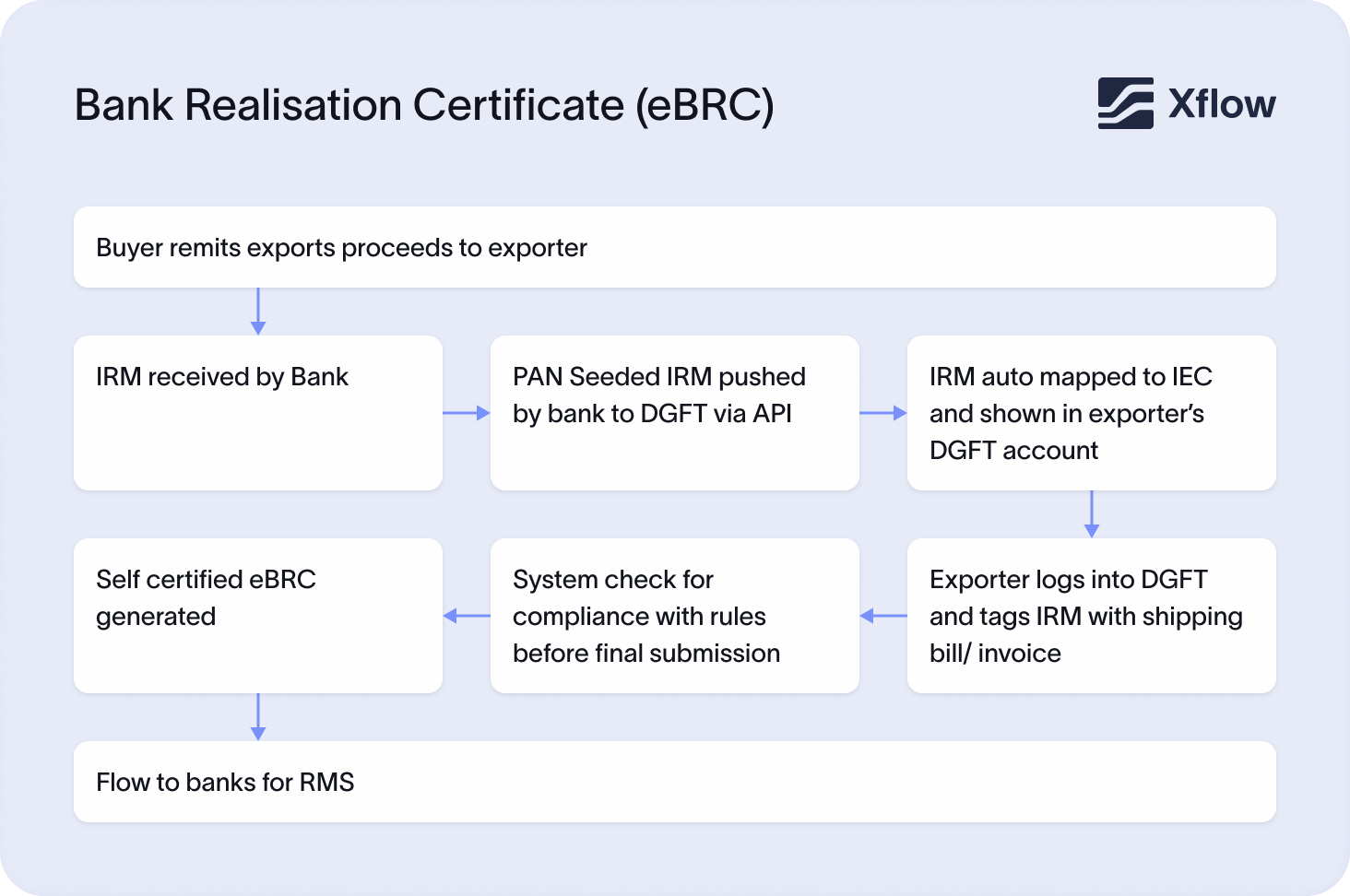
1. Export transaction takes place: The exporter ships goods to a foreign client. Thereafter, they raise an invoice and shipping bill as required under export procedures.
2. Receiving foreign exchange: International payments are received in foreign currency through an authorised bank in India or an online payment platform.
3. Matching of documents by bank: The bank verifies if the foreign inward remittance matches the export transaction. This process involves corroborating the value of the export, the invoice number, and the buyer details.
4. Bank generates e-BRC: After the verification, the bank generates an e-BRC, confirming export receipts.
5. Uploading e-BRC to DGFT portal: The bank then uploads the e-BRC to the DGFT (Directorate General of Foreign Trade) portal. You don’t have to submit it manually.
6. Exporter access: You can log in to the DGFT portal using your credentials and view, download, or print the e-BRC for future use.
What are the documents needed to obtain e-BRC?
To claim incentives under government schemes or complete regulatory compliance, you must obtain an e-bank realisation certificate (e-BRC). Here is a complete list of documents that must be submitted to obtain an e-BRC:
1. Bank account details: IFSC and account number of the receiving bank
2. Exporter information: IEC (Importer–Exporter Code) and name and address of the exporter (usually auto-filled in DGFT portal)
3. Shipping bill/export invoice details: Shipping bill number, date, port and currency, invoice value, and invoice code.
How to download a BRC?
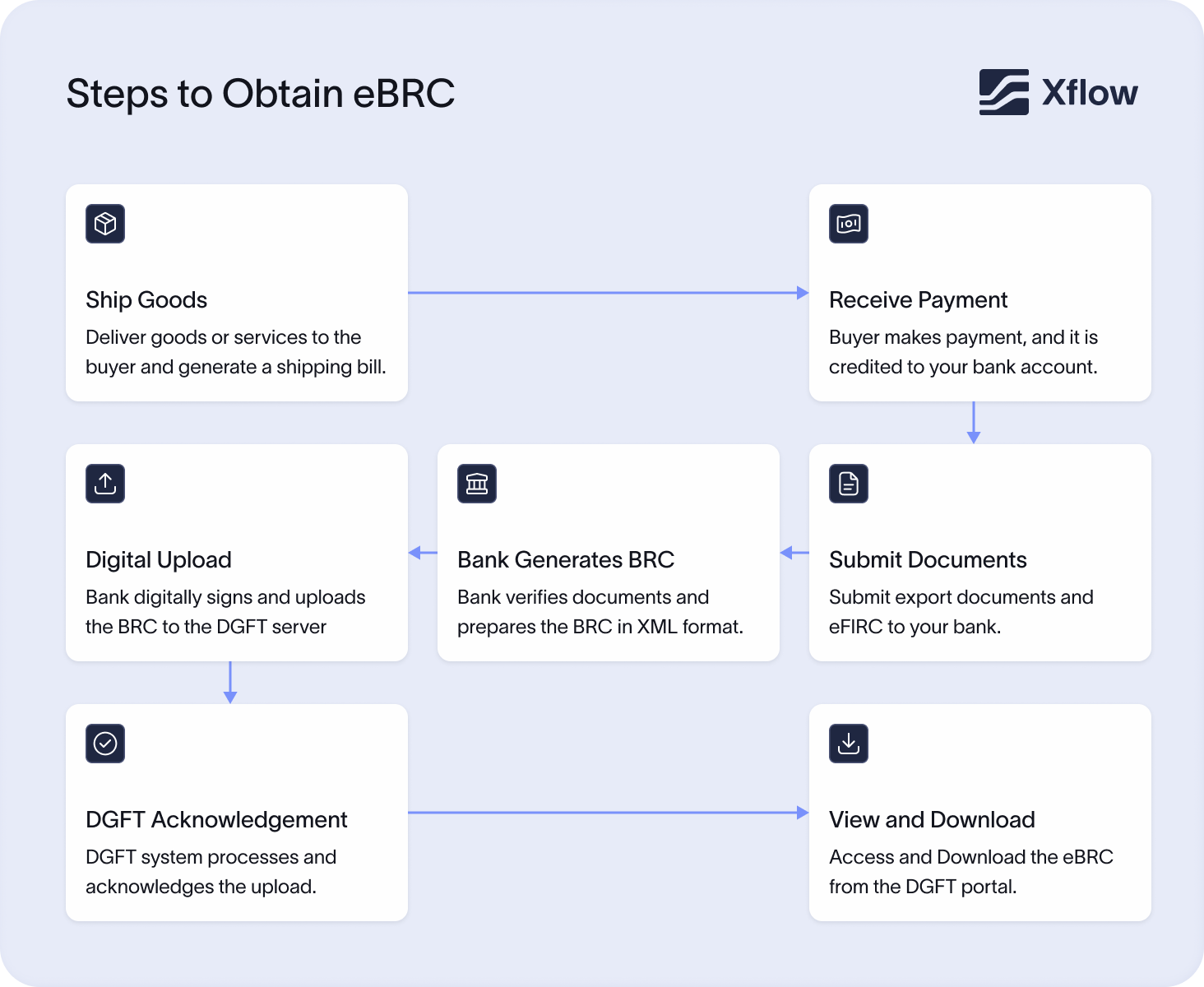
Here is a step-by-step process for downloading a BRC:
1. Visit the DGFT portal - Visit https://dgft.gov.in.
2. Login - Use the exporter’s IEC number and password to log in.
3. Visit the e-BRC section - Find the option for “e-BRC / Bank Realisation Certificate” on the dashboard.
4. Enter export details - Fill in details such as the shipping bill number, export date, and IEC.
5. Search for BRC - The system will display available e-BRCs uploaded by the bank.
6. Download BRC - Click on the download button to get the e-BRC in PDF format.
7. Save/ Print - Save the file for records and print if needed.
How do we claim incentives for exports using e-BRC?
The e-BRC helps exporters unlock different benefits from their international trade. Apart from serving as proof of payment, e-BRC also helps claim various government benefits, such as MEIS, SEIS, and RoDTEP. Here’s how you can claim incentives using e-BRC:
1. Download e-BRC: Get the electronic bank realisation certificate from the DGFT portal.
2. Check for eligibility: Use your e-BRC to apply for various export incentive schemes like the Service Export from India Scheme (SEIS) and confirm your eligibility.
3. Submit required documents: Along with the e-BRC, provide other export documents, such as shipping bills, invoices, and bills of lading, that are linked with the e-BRC.
4. Submit details on the ICEGATE platform: Exporters should submit their shipping invoices on the Indian Customs Electronic Data Interchange Gateway (ICEGATE) platform, which automatically shares them with DGFT.
5. DGFT matches FOB Value: Once the details are submitted by the exporter, DGFT decides the incentive that needs to be provided. This is done by matching the Free on Board (FOB) value of the exported goods, as shown in the shipping bill, against the export mentioned in the e-BRC.
The bottom line
The Bank Realisation Certificate is official proof that payment for exports has been received in foreign currency. Knowing what it means and how you can obtain it is essential for claiming government benefits and ensuring regulatory compliance.
For exporters involved in cross-border transactions, Xflow offers seamless solutions for receiving international payments. It enables faster settlements, often within just one business day, and allows you to save 50% on foreign exchange rates without the hidden markups that typically eat into your profits.
Xflow also simplifies compliance by automatically generating essential documents, such as eFIRA and FIRC, helping you stay audit-ready with minimal stress. Plus, with Xflow’s FIRC calculator, you can receive a transparent breakdown of actual costs and potential savings on your transactions, ensuring accurate financial assessment.
Sign up today to simplify your global transactions with Xflow!
Frequently asked questions
You can get BRC by submitting the export documents to your bank. The bank will file them with the DGFT portal. Once verified, the bank issues the BRC (Bank Realisation Certificate).
Exporters receiving foreign payments must obtain a Bank Reference Certificate (BRC) to validate inward remittance and claim export benefits under various government schemes.
Yes, BRC is mandatory for exporters to prove foreign payment receipts and comply with RBI and DGFT regulations.
An e-BRC confirms export payment realisation against the shipping bills of exports, while an eFIRC (Electronic Foreign Inward Remittance Certificate) is issued by banks against any receipt of an amount by exporters in a foreign currency in exchange for their exports.
Contact your bank with supporting documents (such as an invoice or shipping bill) to request corrections in the e-BRC on the DGFT portal.