Introduction
From the ancient Silk Road days to our current digital age, the way we record trade has undergone significant changes. The way businesses keep track of sales has come a long way. For Indian businesses that sell their products globally, an export invoice is the most important piece of documentation. It’s what helps you send products, handle payments, and follow all the different rules when doing business internationally.
In this article, we’ll explore the various aspects related to commercial invoice for export, including what it is, why it’s needed, the time limit for raising one, different types, and its essential contents.
What is an Export Invoice?
An export invoice is a detailed document that an Indian business (exporter) issues to the recipient importer in a different country, when selling goods internationally. An export invoice is an official proof of the transaction, laying out exactly what was sold, to whom, for what price, and under what conditions. It also states how much the importer owes to the exporter.
Why is an Export Invoice needed?
The importance of export invoice goes beyond simply meeting legal requirements. This document is fundamental for Indian businesses engaged in international trade, serving several critical functions:
- Legal Proof: A commercial invoice for export is official proof that proves a business has made a sale. It clearly shows what was sold, its cost, and the agreed terms between an Indian business and a foreign buyer. It serves as a crucial document to refer to in the event of any disagreements between the parties.
- Smooth Customs Checks: The information on a commercial invoice for export is of utmost importance to customs officials in both India and the destination country, enabling them to understand the shipment and calculate any applicable taxes or duties. This means your goods clear through customs without a fuss.
- Help with Insurance Claims: In case the goods get lost or damaged on their journey, the export invoice serves as evidence to help you make a claim with your insurance company to get your money back.
- Fair Tax and Duty Calculation: Government departments use the export invoice to work out the correct taxes and duties on your exported goods. This keeps everything fair and open in international trade.
- Getting the Money Home: If any Indian business has trouble getting paid from abroad, the export invoice can be used when talking to officials of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to get help bringing your money back into the country.
- Record-keeping: The export invoice is a crucial record for both the exporter’s accounts and for the buyer’s. It’s also great for tracking the performance of your international sales.
Time limit to raise an Export Invoice
According to the rules of the Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017, the time limit to raise export invoices in different cases would be:
| When the supply involves the movement of goods | When the supply involves the provision of services | For goods sent for sale on an approval basis |
|---|---|---|
| The invoice should be issued before or at the time of removal of the goods for delivery. | The invoice should be issued before the provision of service or within a specified time (60 days) after the provision of services. | The invoice must be issued at the earlier of the following two cases: If approval is received within 6 months, the invoice date is the approval date. If approval is not received within 6 months and the buyer hasn’t intimated refusal, the invoice date is the expiry of the 6 months. |
Types of Export Invoices
The various types of export invoices are:
- Commercial Invoice: A commercial invoice for export is the most common document that serves as the actual bill of sale from the Indian seller to the foreign buyer. It provides all the details of the transaction, including the goods sold, quantities, prices, and terms, which are essential for customs clearance and payment processing.
- Proforma Invoice: Issued by the Indian exporter before a confirmed order, proforma invoice is a detailed quotation that outlines the estimated costs, terms of sale, and payment conditions, allowing the foreign buyer to make informed decisions, secure import licenses, or arrange financing prior to placing a firm order.
- Consular Invoice: Required by certain importing countries, this is a commercial invoice that needs to be certified by the consulate of the importing nation located in India. Its purpose is to verify the authenticity, value, and origin of the goods, helping the importing country ensure proper duty assessment and compliance with their specific import rules.
- Legalised Invoice: A legalised invoice is similar to the consular one, but it differs in format flexibility. This type of invoice is usually required in Middle Eastern countries. While it doesn’t follow a predetermined format like the consular invoice, it serves a similar purpose of verifying the document’s authenticity for customs clearance.
- Customs Invoice: In some cases, the customs authorities of the importing country might require a specific invoice format provided by them, rather than a standard commercial invoice. This document typically contains details similar to a commercial invoice but might include additional information tailored to their particular customs procedures, aiding in their assessment and duty collection.
In addition to the standard export invoice types, Indian exporters must issue a GST-compliant tax invoice when supplying goods or services for export. This invoice is crucial for complying with GST regulations. It also enables exporters to claim Input Tax Credit (ITC) on export-related expenses.
So, to claim these benefits under the GST regime, exporters must comply with one of the following three regulatory frameworks:
- Export with Payment of IGST: In this method, the exporter charges Integrated GST (IGST) on the invoice and remits it to the government. The tax paid can subsequently be claimed as a refund. The commercial invoice must indicate the IGST amount and include a declaration “Export with payment of IGST under Rule 96 of the CGST Rules.”
- Export under Bond or LUT (without Payment of IGST): Under this, the exporter does not charge IGST but is required to furnish a Bond or Letter of Undertaking (LUT) to the GST authorities, declaring compliance with export regulations. Regular exporters prefer this option as it avoids the need for upfront tax payments. The commercial invoice must contain a note stating that the supply is made under LUT without payment of IGST.
- Deemed Exports: Deemed exports refer to supplies made within India to notified entities or projects, such as SEZs, that are treated as exports under GST law, even though the goods do not physically leave the country. In such cases, GST is charged on the transaction, and a refund can be claimed by either the supplier or the recipient. A standard tax invoice is issued for these transactions, rather than a traditional export invoice.
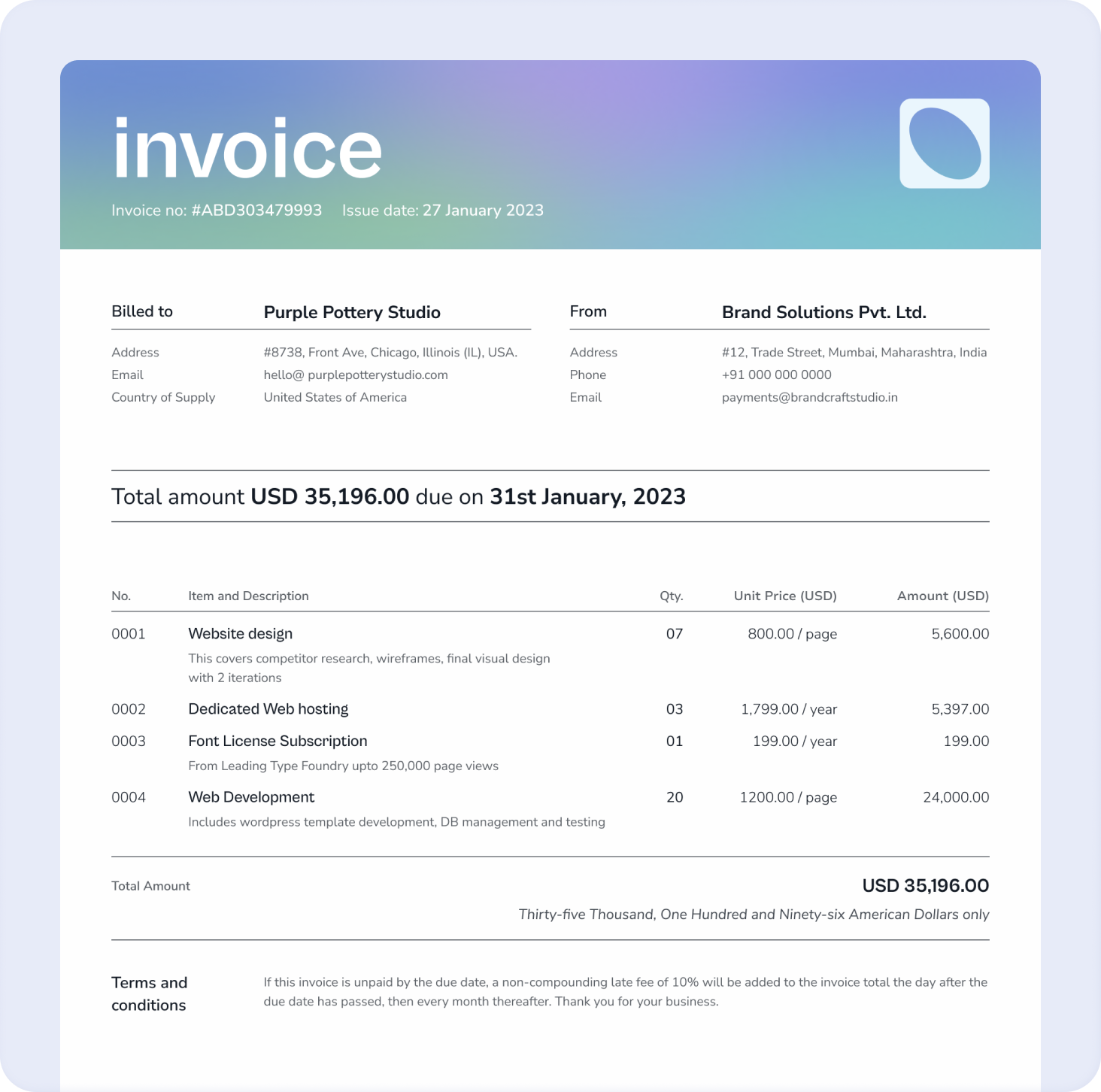
Contents of an Export Invoice
Typically, an export invoice contains the following details:
- Supplier Details: Name, address, contact information, and GSTIN.
- Buyer Details: Name, address, and contact information of the recipient.
- Goods or Services: Details of what is being sold, rates, quantities, and amounts of items sold.
- Invoice Details: Date of generation and a unique, serially arranged invoice number.
- Financials: The conversion rate between currencies, and the total invoice value including insurance details, freight amount and taxes.
- Export Type: Details must include if the export is under bond/LUT, to an SEZ, or with IGST payment.
- Shipping Bill Details: Information related to the filed shipping bill.
- Authorisation: A physical or digital signature of the supplier.
- Additional Notes: Any relevant notes from the supplier to the importer.
How are packing and shipping dealt within an Export Invoice?
Including details related to packing and shipping in an export invoice is not just a requirement but also helps build trust and ensures compliance in international trade. Both of these details enable a smooth export process.
1. Packing Details: These details help customs and buyers verify contents and ensure proper transit packaging. Packing details include the following:
- Type of Packaging: E.g., boxes, crates, pallets.
- Number of Packages: Total count.
- Dimensions and Weight: Size and both gross/net weight per package.
- Markings and Labels: Identifying marks like barcodes or batch numbers.
- Description of Contents: A summary of each package.
2. Shipping Details: Shipping details includes transport and delivery information, like following:
- Mode of Transport: Sea, air, road, or rail.
- Carrier Details: Name of the shipping line or airline.
- Shipping Date: Date of dispatch from the origin port.
- Port of Loading and Destination: Departure and arrival ports.
- Bill of Lading (BOL) or Airway Bill Number: Unique shipment identifier.
Simplify Export Invoicing with Xflow
Is your exporting business struggling with delayed payments, invoice mismatches, or compliance hurdles when dealing with international clients? Xflow helps Indian exporters streamline their export invoicing process and receive foreign payments directly, without hidden fees, US bank accounts, or any regulatory stress. Generate compliant export invoices, track cross-border payments, and save on FX costs, all in one place. Sign up with Xflow today!
Frequently asked questions
A commercial invoice is the primary type of export invoice used in international trade. Every export invoice is a commercial invoice, but not every commercial invoice qualifies as an export invoice unless it contains the required export-specific and regulatory details.
GST does not need to be paid on export invoices in most cases because exports are treated as “zero-rated supplies” under Indian GST law. In fact, exporters can claim a refund of the unutilised Input Tax Credit (ITC) on taxes paid for inputs and input services used in the export of goods and services.
E-invoicing is not mandatory for everyone. E-invoicing is not applicable to government departments or local authorities. Additionally, Special Economic Zones (SEZs) are exempt from generating e-invoices. GST e-invoice limit for turnover more than Rs. 5 Crores applies from 1st August 2023.
Yes, an export invoice is mandatory for service exports to document the transaction and claim GST benefits.
An LUT (Letter of Undertaking) allows exporters to export goods/services without paying IGST and must be referenced on the export invoice.